Hi everyone,
We have some news for you: recently our team has been working hard to put together an Ultimate Guide to Genestack Platform. This guide consists of a general introduction to bioinformatics and the basics of sequencing analysis, as well as a comprehensive set of descriptions of Genestack platform architecture, use cases for various apps, tips and tricks on how to get the most out of the platform and a Q&A section.
We wrote the guide for everyone: whether it's your first of hundredth time doing bioinformatics, we're sure you'll find some useful information there. During the next couple of weeks, before we officially release the guide, we'll publish excerpts from it on our blog. In this post, we will talk about how to choose an appropriate mapper.
On Genestack platform you'll find a range of available mappers.How do you choose the "best" a mapping app“ The answer is: Each aligner is meant to be better used with specific types of data.
Here are our recommendations:
If your data is transcriptomic data (e.g. RNA-Seq), use Spliced Mapping.
For whole genome or whole exome sequencing data:
- If reads are long (>100 bp), we recommend to use Unspliced Mapping with BWA;
- If reads are short, we recommend to use Unspliced Mapping with Bowtie2;
To map bisulfite sequencing data to the whole genome, use Bisulfite Sequencing Mapping.
To map reduced representation bisulfite sequencing data to specific digestion sites on the genome, use Reduced Representation Bisulfite Sequencing Mapping.
More details on various mappers:
Spliced Mapping App This application is based on Tophat2 tool is used to map Raw Reads with transcriptomic data like RNA-seq to a Reference Genome, taking into account splice junctions. Let's take a look at the app page and talk about various parameters: 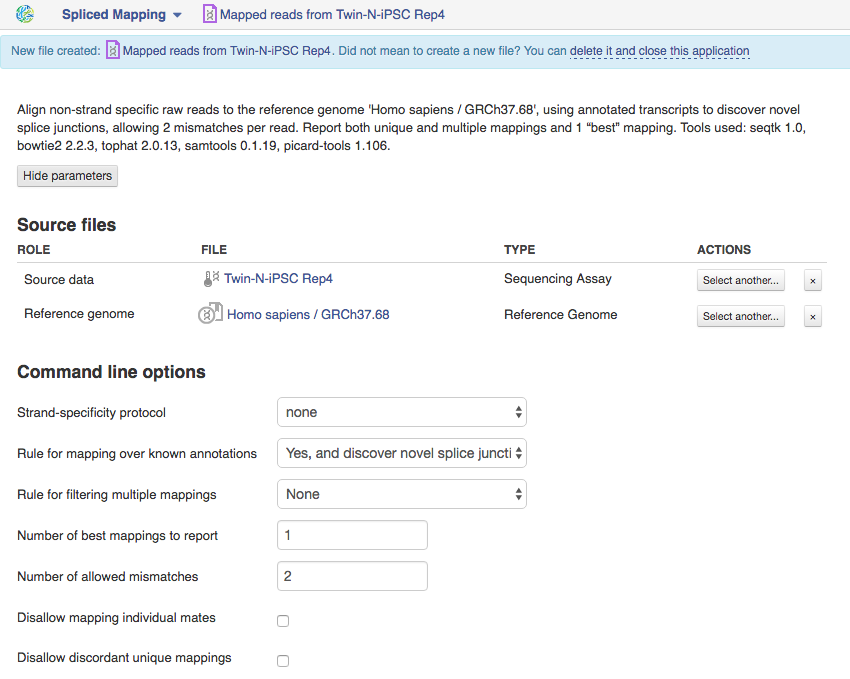 Let's talk a bit about various settings:
Let's talk a bit about various settings:
1)If you are using strand-specific RNA-seq data, the option "Strand-specificity protocol" will let you choose between the "dUTP" and "ligation" method. If you are not sure whether your RNA-seq data is strand-specific or not, you can try using Subsample reads to make a small subsample, map it with Spliced Mapping and check the coverage in Genome Browser for genes on the two strands.
2)By default, the application uses annotated transcripts from the Reference Genome to distinguish between novel and known junctions. Using the option "Rule for mapping over known annotation" you can restrict mappings only across known junctions or infer splice junctions without any reference annotation.
3)With default settings, the application will report the single best mapping for each read, even if there are multiple valid mapping positions. The option "Number of "best" mappings to report" lets you increase the number of reported mappings. This can be used together with "Rule for filtering mappings" to choose whether to keep reads mapping to uniquely or to multiple positions, e.g. report up to 5 possible mappings, and only for multi-hit reads. If you want to be stricter, you can set the number of allowed mismatches from 2 to 1 or 0.
4)For paired reads, using the option "Disallow unique mappings of one mate" you can discard pairs of reads where one mate maps uniquely and the other to multiple positions. Selecting "Disallow discordant mappings" will discard all mappings where the two mates map uniquely but with unexpected orientation, or where the distance between two mapped mates differs from and internally estimated fragment length, including mates mapping to different chromosomes. We used this app in the Testing Differential Gene Expression tutorial that can be found here.
Unspliced Mapping with BWA app
On Genestack, you will find two Unspliced Mapping applications. This one is based on BWA tool and is used to map exome sequencing reads to a Reference Genome and is meant to be used further with our Variant Calling application based on samtools mpileup. 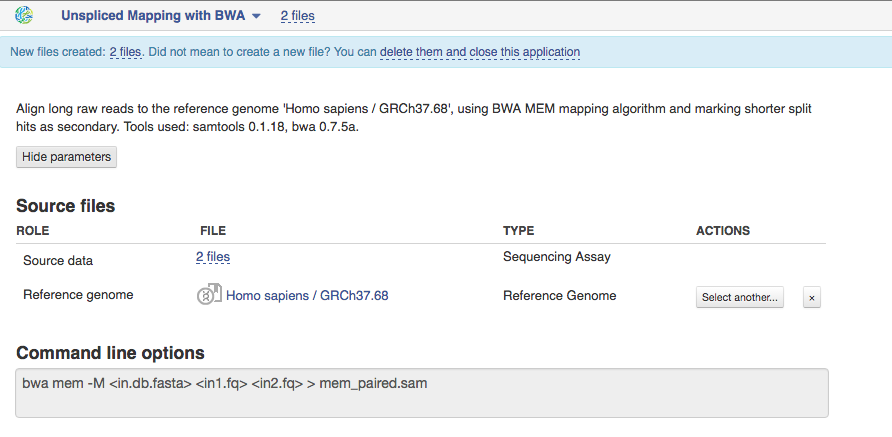 BWA MEM algorithm will be used to map paired or single-ends reads from 70 bp up to 1Mbp ("mem" option in command line). For reads up to 70 bp the algorithm called BWA-backtrack will be applied. This algorithm is implemented with the "aln" command, which produces the suffix array (SA) coordinates of the input reads. Then the application converts these SA coordinates to chromosome coordinates using "samse" command (if your reads are single-end) or "sampe" command (for paired-end reads). We used this app in the Whole Exome Sequencing Data Analysis tutorial that can be found here.
BWA MEM algorithm will be used to map paired or single-ends reads from 70 bp up to 1Mbp ("mem" option in command line). For reads up to 70 bp the algorithm called BWA-backtrack will be applied. This algorithm is implemented with the "aln" command, which produces the suffix array (SA) coordinates of the input reads. Then the application converts these SA coordinates to chromosome coordinates using "samse" command (if your reads are single-end) or "sampe" command (for paired-end reads). We used this app in the Whole Exome Sequencing Data Analysis tutorial that can be found here.
Unspliced Mapping with Bowtie2 app This application is based on Bowtie2 tool and used to map sequencing libraries to a Reference Genome. Suitable sequencing methods include DNA-seq and ChIP-seq. 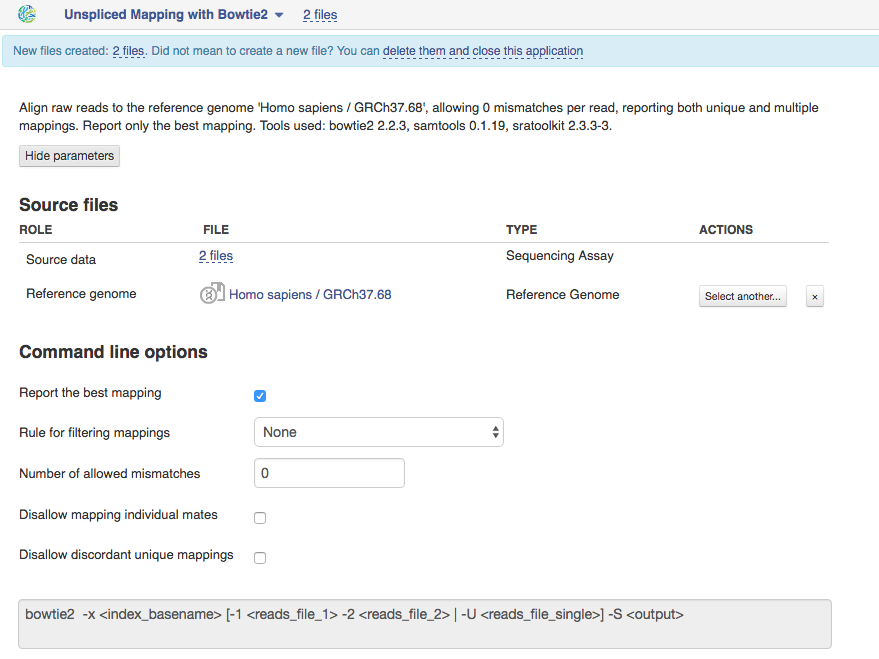 Let's talk a bit about various settings:
Let's talk a bit about various settings:
1)By default the application will report the best mapping for one mappable read. If you are interested in reads mapping to multiple positions, switch off this option and set N mappable positions for one read in the text box "Limit the number of mappings to search".
2)You can apply rule for filtering mappings to choose whether to keep reads mapping uniquely or to multiple positions. If you want to be stricter, you can change the maximum number of allowed mismatches, e.g. if you set it to 1, any mapping with 2 or more mismatches won't be reported.
3)For paired reads, using the option "Disallow unique mappings of one mate" you can discard pairs of reads where one mate maps uniquely and the other to multiple positions. Selecting "Disallow discordant mappings" will discard all mappings where the two mates map uniquely but with unexpected orientation or where the distance between two mapped mates differs from and internally estimated fragment length, including mates mapping to different chromosomes.
Bisulfite Sequencing Mapping app The application is based on BSMAP tool and is used to map high-throughput bisulfite reads at whole genome. Suitable sequencing method is whole genome bisulfite sequencing. 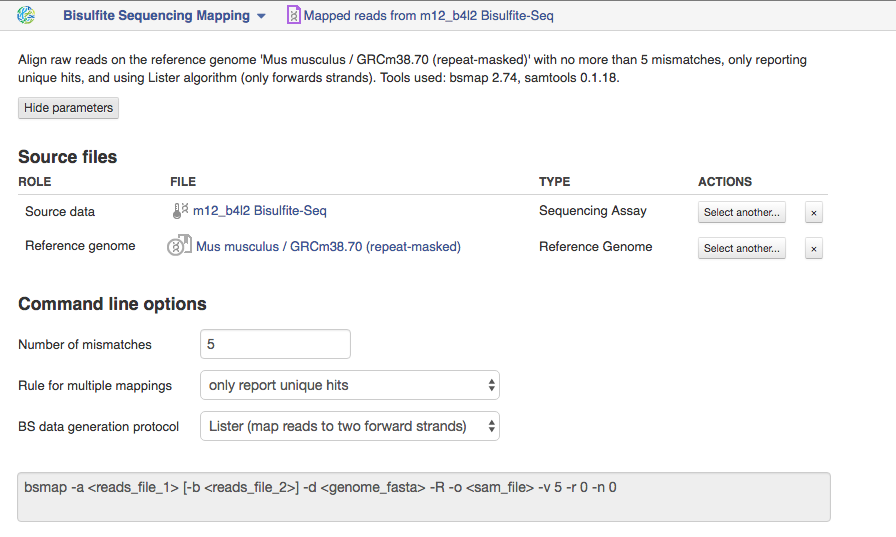 Let's talk a bit about various settings:
Let's talk a bit about various settings:
1)The option "Number of mismatches" lets you set the maximum number of allowed mismatches per read. Changing this number you can affect application runtime and percentage of mapped reads. There is an increase in the percentage of mapped reads and in the application runtime when increasing this value. For example, by default the read could be mapped to the genome with no more than 5 mismatches.
2)By default, the application only report unique hits for one mappable read. But if your reads are mapped to multiple positions in the genome, than you can change rule for multiple mappings to report one random "best" mapping.
3)Depending on the BS data generation protocol that was used to construct the bisulfite converted library, BS reads may be analysed in different ways. According to "Lister" protocol, your reads will be mapped to two forward strands. Read more about this protocol in the study of Lister et al. [1]. Choosing the "Cokus" protocol the application will align your reads to all four strands. You can find more details about this protocol in the original study of Cokus et al. [2]. We used this app in the Methylation Profiling Using Genestack Platform tutorial that can be accessed here.
Reduced Representation Bisulfite Sequencing Mapping The application is based on BSMAP tool and is used for mapping reduced representation bisulfite sequencing reads to the specific digestion sites on genome. Suitable sequencing method is reduced representation bisulfite sequencing. 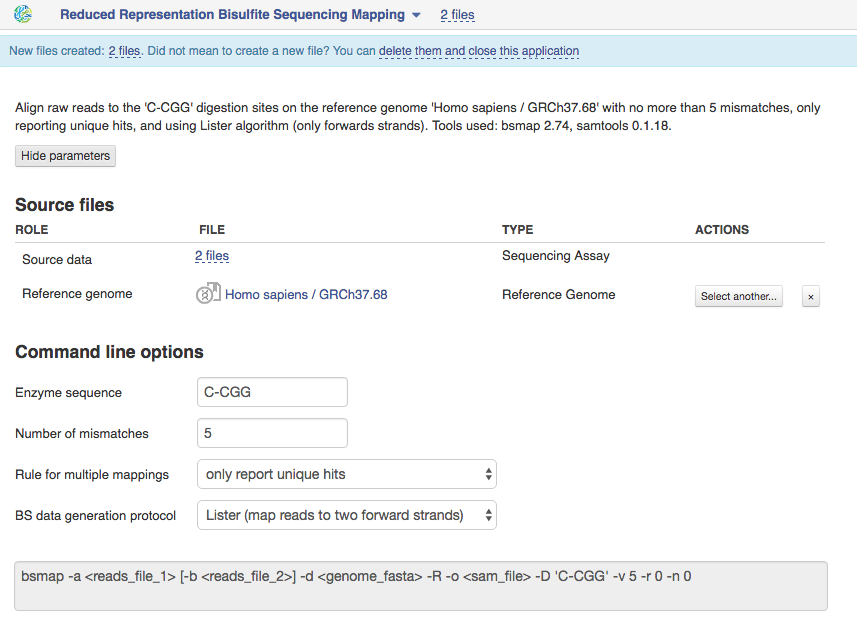 Let's talk a bit about various settings:
Let's talk a bit about various settings:
1)You should set "Enzyme sequence" which was recognized by specific restriction enzyme to digest genomic DNA in the process of library preparation. By default, the application uses 'C-CGG' sequence for MspI restriction.
2)The option "Number of mismatches" lets you set the maximum number of allowed mismatches per read. Decreasing this number you can reduce application runtime and percentage of mapped reads. By default the application aligns reads to the reference genome with no more than 5 mismatches.
3)By default the application only report unique hits for one mappable read. You can change rule for multiple mappings to report one random "best" mapping, if your reads are mapped to multiple positions in the genome. Choose the BS data generation protocol that was used to construct the bisulfite converted library. If it is the Lister protocol [1], than your reads will be mapped to two forward strands. Reads generated using the Cokus experimental protocol [2] will be aligned to all four strands. To find a previous extract from the Ultimate Guide to Genestack platform, go here.
Next week's post will describe various reference genomes available on the platform, and how to choose the most appropriate one for you. We hope you enjoyed this post, please let us know your thoughts by commenting below. If you want to get in touch with our team, you can do this using the chat window on the platform or emailing us at contact@genestack.com. References:
- Lister R, Pelizzola M, Dowen RH, Hawkins RD, Hon G, Tonti-Filippini J, Nery JR, Lee L, Ye Z, Ngo Q-M, Edsall L, Antosiewicz-Bourget J, Stewart R, Ruotti V, Millar AH, Thomson JA, Ren B, Ecker JR. "Human DNA methylomes at base resolution show widespread epigenomic differences." Nature. 2009 462(7271):315-22.
- Cokus SJ, Feng S, Zhang X, Chen Z, Merriman B, Haudenschild CD, Pradhan S, Nelson SF, Pellegrini M, Jacobsen SE. "Shotgun bisulphite sequencing of the Arabidopsis genome reveals DNA methylation patterning." Nature. 2008 452(7184):215-219.